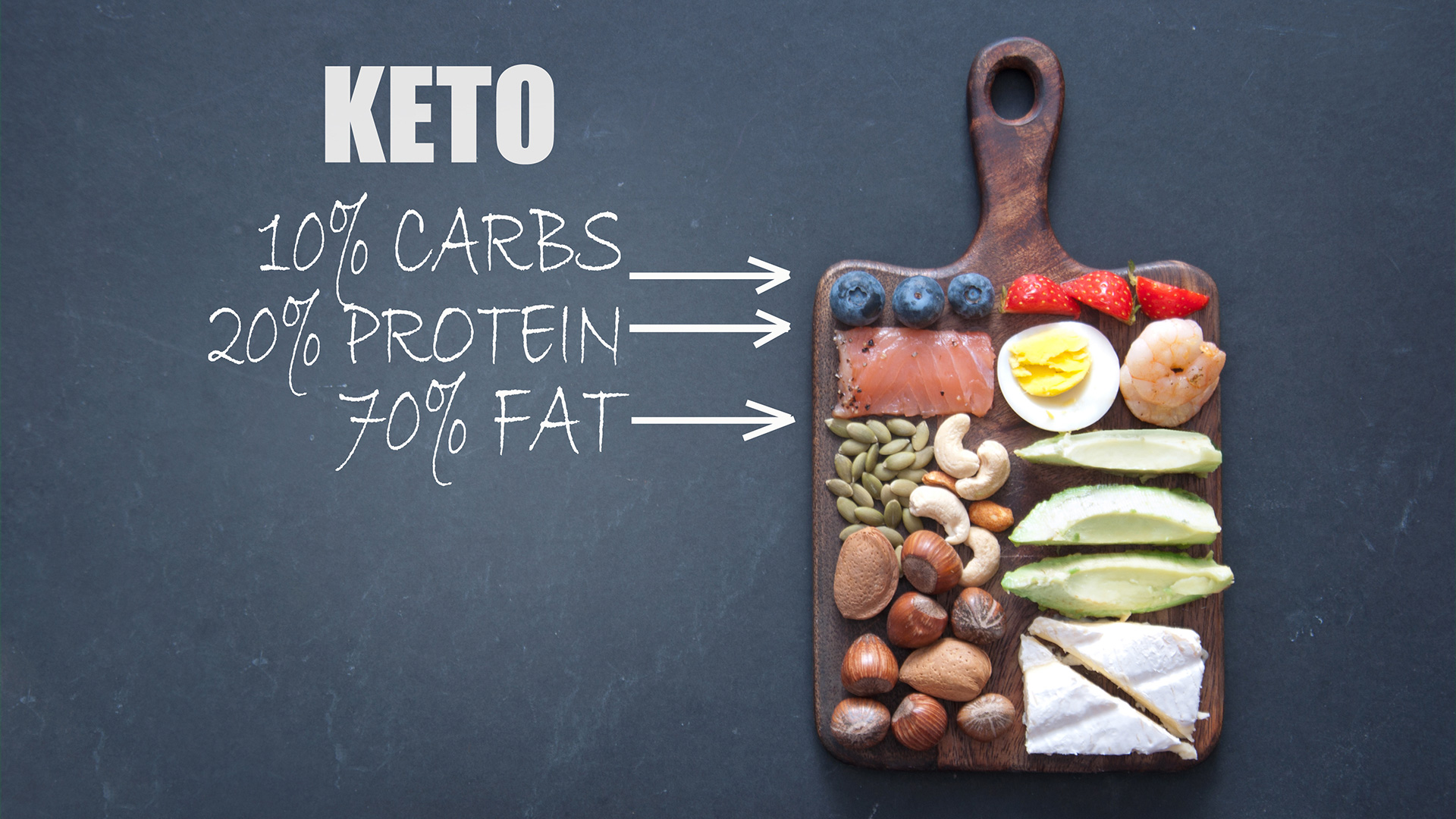
Our bodies are built to be flexible machines. They can burn both sugar (glucose) and fat for energy, switching between the two depending on what’s available. The problem? In today’s world of constant snacking and carb-heavy meals, most people stay stuck in glucose-burning mode all day long, and that’s not always a good thing.
Glucose: Your Body’s Quick, Easy Fuel
Think of glucose like gasoline: fast, powerful, and convenient.
Here’s how it works:
- You eat carbs: bread, pasta, fruit, sugar, you name it.
- Your body breaks them down into glucose, which enters your bloodstream.
- Your pancreas releases insulin, the hormone that moves glucose into your cells for energy.
- Any extra glucose gets stored in your liver and muscles as glycogen or turned into fat for long-term storage.
Your body loves glucose because it’s quick to use. That’s why sugary snacks give you an instant pick-me-up. But it burns out just as fast, leading to energy crashes, mood swings, and hunger soon after.
If you’re constantly eating carbs, your body never gets the chance to switch gears and burn fat for energy.
Fat: The Long-Lasting, Steady Energy Source
Now let’s talk about fat, the slow-burning log on your metabolic fire.
When you go without carbs for a while (like during fasting or a low-carb diet), your glucose levels drop. Your body begins breaking down stored fat into fatty acids, and your liver converts them into ketones,a clean, efficient fuel for your brain and muscles.
That’s ketosis, the magic behind the ketogenic diet.
Fat doesn’t cause energy crashes. It provides stable energy for hours, which is why people on keto often say they feel more alert, more focused, and less hungry.
Ketosis: Your Fat-Burning Superpower
The ketogenic diet trains your body to rely primarily on fat for energy instead of sugar. Once you’re “fat-adapted,” your body becomes incredibly efficient at:
- Burning stored fat for fuel
- Producing clean, brain-boosting ketones
- Reducing hunger and sugar cravings
That’s why keto followers often describe the experience as steady, calm, and clear-headed—because their energy doesn’t spike and crash with every meal.
How Fasting Helps You Burn Fat
Ever wonder why people talk about intermittent fasting? It’s because when you go for long stretches without eating, your body naturally shifts into fat-burning mode:
- After 4–6 hours without food, your body starts using stored glucose.
- After 12–24 hours, your glucose stores run low, and your body burns more fat for fuel.
- After 24+ hours, you’re in deep fat-burning mode and producing even more ketones.
This is why fasting (or cutting back on carbs) can help with weight loss—it forces your body to tap into its fat reserves instead of relying on constant sugar refills.
Bottom Line: Train Your Body to Burn Fat
Our bodies were designed to burn both sugar and fat—but in a world full of constant carb availability, we’ve forgotten how to use our fat-burning system.
By reducing carbs, embracing the ketogenic diet, or simply spacing out meals with intermittent fasting, you can help your body:
- Burn fat more efficiently
- Stabilize energy throughout the day
- Improve focus and mood
- Support long-term weight management
Your body already knows how to do it. You just have to give it the chance.